Working toward your run-to-retire or run-to-conversion plant strategy? Our team can collaborate with you to develop a custom run-to-retire or run-to-conversion service strategy based on your ROI goals, and remaining operating life cycle. Find out how.
The Power of YES.
Can GE Vernova's Steam Power team partner with me on a run-to-retire strategy?
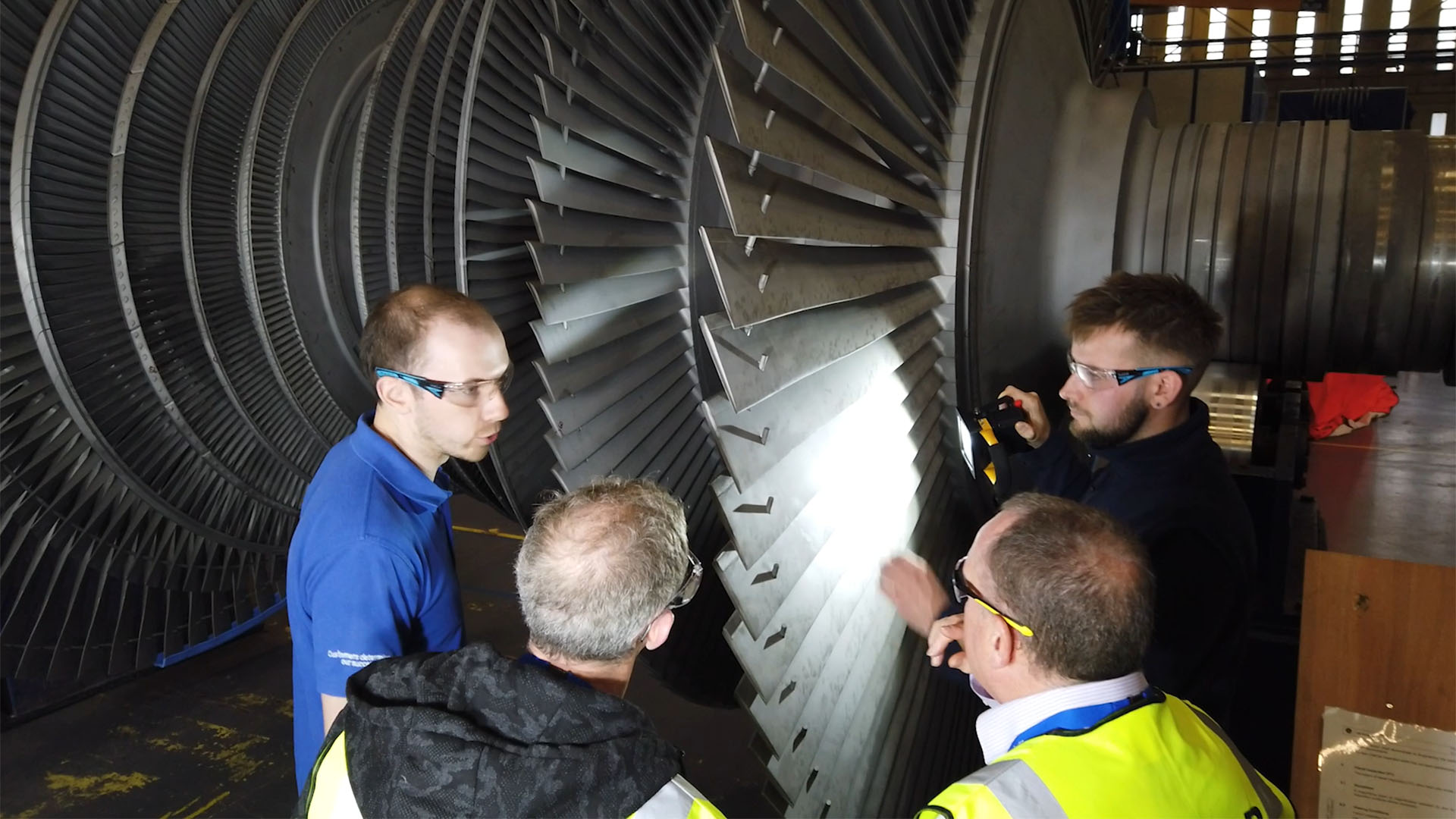

YES. If you’re approaching the period of considering a run-to-retire or run-to-conversion operating strategy for your plant, there are numerous factors to consider… among them, partnering with a service provider that can help you:
- Squeeze the most remaining life from your existing equipment
- Assess/reduce the risks of operating to the boundaries of your assets
- Optimize the return on investment during your remaining life cycle AND decommissioning or conversion activities
There’s likely not a more important time in your life cycle to leverage OEM experience than when planning and executing a run-to-retire strategy.
Continued partnership
That's where our Steam Power team comes in
We stand ready to be your energy transition partner through the latter years of your operation with:
Frequently asked questions
Energy transition partner FAQs
ADAPTING FOR THE ENERGY TRANSITION
What is GE Vernova's Steam Power doing to be more nimble and quick with the core services you provide?
In the spirit of continuous improvement, our team is focusing on several areas to build on our service capabilities to support steam plant operators through the energy transition, including:
- Developing in-house manufacturing capabilities in our service center network (select locations/regions) for components such as generator stator bars to reduce the cycle time of generator rewinds
- Collaborating with key suppliers to deliver certain parts faster than they have before... as example, we’ve slashed the delivery cycle time of select steam turbine blades by as much as four months
- Introducing advanced new robotic inspection technologies allowing our team to identify higher risk equipment ‘hot spots’
- Continuing to optimize our emergency response capabilities by improving the cycle times across all activities, from ‘on-the-ground’ solutioning and proposals through parts delivery, resource mobilization and repairs execution
What is GE Vernova doing to help steam operators with a limited remaining life cycle to plan for what’s next?
We’ve developed a new asset management program that focuses on supporting plant operations that have identified general time horizons for their remaining operating life in their current configuration. Whether a site plans to shut down or convert their site within just a few years, or looking for another 10-15 years of operation, this program is designed to help operators:
- Understand how much more life their plant equipment has left
- Identify a custom service strategy for their remaining life cycle and ROI goals
- Integrate a risk management strategy to help ensure their reliability and safety
- Calculate the economics of options for what comes next... whether staying in cold reserve, converting to a gas or other configuration, or shutting down and repurposing assets
What is the best risk management strategy for a steam plant today navigating the energy transition?
While numerous factors feed into an effective risk management strategy, one of the most effective technologies you can tap into is asset monitoring software. Using sensor technologies, these services can help you cost-effectively:
- Detect operating anomalies/early failure modes in real time (e.g., Temperatures, vibrations, stress points)
- Identify changing boundary conditions affecting equipment life (e.g., Corrosion, fatigue, creep)
- Reduce risks of forced shutdown from aging assets
- Plan outages with more precision and predict emergent work
Common issues for aging equipment FAQs
STEAM TURBINE SERVICES
What are common issues for aging steam turbine units?
For steam turbines, rotor or last stage blade cracking are among the more common risks with aging units/parts. These can also have the most significant impact on your operation in terms of a forced shutdown or potential safety issues.
Other common age-related issues include:
- Steam valve damage
- Outer casing damage
- Diaphragm creep
- Component brittlement
- Lubricant life
- Auxiliary systems end of life—including coolers
Understanding the operating boundaries of individual components in your steam turbine can help you better anticipate potential issues, as well as plan for emergent work that may be discovered during a planned outage.
Are there differences between potential risks for rotor issues in the HP/IP and LP sections of the unit?
In the HP/IP section, cracking or creep can be caused by cycling in terms of starts/stops or load changes, as well as high temperatures. In the LP section, surface pitting or corrosion in crevices can cause similar cracking or creep issues.
- Severity of cracks or creeping can be determined by assessing a sample of the rotor or conducting non-destructive testing, which in some cases can be done on site. These analyses can help determine the remaining life of the rotor, and a viable repair solution in many cases.
- For older un-bored rotors, an ultrasonic inspection can be conducted to pinpoint hard-to-access high-stress areas on the unit
Given the cost of replacing last stage blades, are there any other options if they show signs of damage?
Yes. First, non-destructive testing can be performed- in some cases on site- to determine if a last-stage blade can continue to be used in operation safely. If not, one option is having a thermal study performed to determine the impact of removing the blade(s) and operating without them. This will result in performance loss, but can be an option to safely resume your operation faster with temporary modifications. There are similar service options for both rotating or stationary blades/buckets.
What services can be done to a unit’s casing to avoid a full replacement?
In the inner casing, material loss can occur over time due to corrosion. To prevent further loss and if the casing is deemed to still be safely operable, a weld repair or erosion protection ring can be installed.
On the outer casing, cracks or deformation can occur from several factors. On site welding can address such issues in some cases, while others may also require additional machining which is typically performed in a repair shop.
What spare parts for steam turbines are most essential to have?
Essential emergency spare parts for steam turbines include bolting hardware and valve internals. While Steam Power maintains a stock of certain components, inventory availability varies. Therefore, anticipating and proactively planning for more commonly known parts issues related to wear and tear or aging helps reduce the incidence of failures, as well as keep outage schedules on track.
What is the recommended approach for repairing steam turbine joint leaks in the HP and IP sections?
Addressing steam joint leaks is crucial due to the potential danger posed to personnel, and it requires a system-level strategy. This includes diagnosing the root cause, making repairs such as bolting upgrades, steam dams, sealants, or half-joint repairs, and potentially machining the joint and boring internal fits to restore flatness and prevent leaks. Quick and reliable repairs are also essential when considering the impact of steam leaks into the atmosphere.
How can you determine if a rotor life extension makes sense for your steam plant?
The best way to assess the ROI of a rotor life extension is to examine your operating profile within the context of your expected remaining life cycle. If your operation is more cyclical, you may want to do a starts-based calculation to determine how much more time a life extension will deliver to your operation. If you run your site longer periods of time without shutting down, an hours-based approach probably makes the most sense to understand your life extension ROI. Our team can collaborate with you to help calculate the benefits of a rotor life extension based on your specific operating profile.
GENERATOR SERVICES
What are common issues for aging generator units?
For generators, rotor/stator winding degradation, along with seal/cooler leakage account for ~80% of aging unit issues. Others include:
- Exciter flash over
- HV bushing failure
- H2 seal wear/leakage
- Cooler leakage
- Auxiliary systems end of life
Understanding the operating boundaries of individual components in your generator can help you better anticipate potential issues as well as plan for emergent work that may be discovered during the course of a planned outage.
What stator issues pose the most risk to my steam plant operation?
- A stator bar ground fault can lead to a forced outage from a system protection trip.
- Leakage in the stator can result in hydrogen getting into the water which is a safety risk, or water can seep onto the stator bars.
- Damage to the stator core can also lead to a forced shutdown.
Repair and parts replacement solutions can address these issues, but an effective preventive action to avoid them is using software monitoring and/or inspection services to pinpoint emerging issues before they become serious.
What causes an exciter flash over, and what damage can it do?
An exciter flash over is triggered by a progressive loss of contact between the rings and brushes. This can be caused by dirt contamination, worn brushes, vibrations or plugged vents. A flash over can burn out certain components which then need to be replaced. The best ways to prevent this from occurring is to replace brush holders when their springs are aging, or to polish/turn slip ring surfaces through machining which can be conducted on site.
What are the most common signs of a faulty generator rotor?
Some common signs include:
- Shorted turns
- Vibration issues
- Excitation current increases to maintain output
- Inability to maintain output due to excitation limitations
How can you determine if a generator rotor life extension makes sense for your steam plant?
The best way to assess the ROI of a rotor life extension is to examine your operating profile within the context of your expected remaining life cycle. If your operation is more cyclical, you may want to do a starts-based calculation to determine how much more time a life extension will deliver to your operation. If you run your site longer periods of time without shutting down, an hours-based approach probably makes the most sense to understand your life extension ROI. Our team can collaborate with you to help calculate the benefits of a rotor life extension based on your specific operating profile.
When replacing or exchanging a generator rotor, are there other components or accessories that need to be replaced/modified with it?
Depending on configuration, some units don’t require other component replacements/modifications when replacing or exchanging a generator rotor. If any are needed, they commonly include:
- Oil deflectors
- Bearings
- Hydrogen seals
- Excitation system settings
What causes a winding short, and what is needed to repair it?
The degradation of insulation- which can be accelerated by oil contamination- can trigger a winding short. Copper distortion or connection issues can also cause this issue. Aging, along with more cyclical operation can be contributing factors to a winding short.
There are several repair solutions for a winding short including a full or partial rewind either on site or in a repair shop- this can be done with either existing or new copper. The additional benefits of a shop repair include the potential for faster, less costly work scope due to having an established, controlled work environment.
How long does it take to repair a generator rotor winding?
Cycle time for a winding repair varies depending on the scope required. A pre-planned full field rewind takes, on average, approximately 30 days. However, some repairs can be performed in as little as 1-2 weeks. Rewinds related to forced outages typically take longer when new parts/materials need to be ordered.
Managing your controls system
SERVICE STRATEGY/CAPABILITIES
How can GE Vernova's Steam Power business help you limit the costs of your controls services?
While we believe that maintaining your controls as a holistic system will deliver the best life cycle outcomes, we recognize that operators in later life cycle stages need to limit their maintenance costs.
With the ability to deliver individual components (including HMIs, controllers, cards and CPUs), we can help limit the scope of service work, which may result in lower project costs. By designing our parts with the compatibility for this ‘a-la-carte’ type of maintenance, our team can help ensure that your controls system has obsolescence protection with cost-effective services. For fleet-level operators, we can collaborate on end-to-end controls packages - featuring our most advanced technologies - to support your plant systems holistically and efficiently.
What is GE Vernova doing to help operators optimize their controls life cycle management?
We continue investing in a holistic platform of resources to help you optimize your controls systems throughout their life cycles. They include:
- Notification & delivery of software updates
- Preventive maintenance recommendations
- Cyber security assessments
- Cyber security updates/alerts
- Option for a controls ‘resident engineer’ on site
- Technical information letter (TIL) program
- Parts program
- Training
- 24/7 technical support
We’re also developing a dashboard that will provide visibility to your hardware and software life cycles, as well as your software vulnerability status. To help you plan for maintenance actions, this portal will also provide recommended software updates, both from obsolescence and vulnerability perspectives.
What controls maintenance work is recommended during an outage?
We recommend that your steam plant’s control system be assessed every year by either our service team or yours. This includes performing a system backup and restore, in addition to addressing any issues that may be seen. Our team can perform this scope during the course of a planned (or unplanned) outage for more efficient maintenance. In fact, some of our field engineers that service steam turbine and generator equipment can also service your controls during the same visit to your site.
What are the most important preventive measures to stay on top of when it comes to controls maintenance?
As with most technologies, taking a preventive approach to servicing your controls system will likely result in the most efficient life cycle costs and performance. Some key preventive actions include:
- Integrating your overall maintenance strategy into your outage cycle planning
- Identifying actions to address recent system alarms
- Testing for potential power supply failures or ground faults
- Taking a site-specific approach to cyber security with recommended patches and updates
- Assessing spares and obsolescence options
- Informal training/coaching as needed based on your evolving workforce
What are some common preventive maintenance activities operators can perform independently?
An effective independent maintenance program should start with reviewing our GEH-6721 volume 2 guide, which provides instructions on Mark* VIe maintenance including panel cleaning, cooling fans check, maintaining temperature, terminal tightening, air filters cleaning, review of diagnostics logs and execution of corrective actions.
You can also do an obsolescence evaluation to understand your future parts needs. In addition, review all applicable Technical Information Letters (TILs) that we’ve posted and implement them as recommended. Of course, our service team can assist with these activities as needed.
Can GE Vernova help with your spare parts strategy?
Absolutely. We have several resources that can support your spare parts strategies. The first step is to understand which control systems you have, and where they are in their life cycle. Our parts experts can help by performing a spare parts assessment of your existing spares to help ensure they are the latest revision, and are still applicable for your controls system. Recommendations can then be made for critical spare parts and recommended actions for your existing spare parts.
If we upgrade to new GE Vernova controls technologies, will we be able to use the spare parts we’ve purchased previously?
We’ve designed our newer controls systems to be compatible with many components designed for previous versions to help limit your life cycle costs, and offer more maintenance flexibility. There are some limitations on new parts availability with certain systems such as Mark* V controls, however, we do have limited refurbished parts available, as well as options for repairs and replacement exchanges.
Does GE Vernova still service controls technologies on its legacy brands?
Yes. Our service team continues to support both OEM and legacy brand controls systems including the Mark* VIe and ALSPA systems. Our portfolio for both platforms includes core services and life extension solutions, along with current cyber security technologies to help protect your plant’s ecosystem.
Do you still support Mark* V controls systems?
The Mark* V system is not produced anymore, so new parts are not available. We do have limited refurbished parts available, as well as options for repairs and replacement exchange. We also have OEM factory-trained field engineering resources for your service needs. In addition to ongoing support, an existing Mark* V can be replaced in full with a new Mark* VIe control. A Mark* VIe control offers many advantages over the legacy Mark* V control, including a distributed control architecture, reduced footprint, enhanced computing, and simpler product structure.
Do you offer training on your controls systems?
Yes, our team provides in-person and remote training on our controls systems. In addition, using our virtual controller software, you can have a safe environment at your site for testing and training on control system activities.
If you’re interested in having a Steam Power consultant help your team maintain your controls system, we can provide you with a dedicated expert to help with activities including:
- Pre-outage assessments
- Spares and obsolescence assessments
- Preventive maintenance assessments
- Operational productivity assessments
- Cyber security assessments
CYBERSECURITY
How can Steam Power help you stay ahead of cyber threats in today’s environment?
We can partner with you to provide OT-specific cybersecurity assessments based on the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Top 18 Security Controls, with multiple levels to meet your unique needs. Implementing just the first five of these controls can reduce your risk of cyber attack by up to 85%.
Additionally, patching your systems is essential to protect your assets. Our patch validation program provides monthly operating system and application patches, as well as antivirus and intrusion-detection signature updates for human-machine interfaces (HMIs), servers, switches, and network intrusion-detection devices. Monthly updates can be applied to individual HMIs or via the SecurityST appliance for network-wide deployment.
And, our team posts security updates—for all of our controls platforms—on our public website as they become available to help you stay informed on current events in cybersecurity. As part of your ongoing efforts, we recommend that you do a cybersecurity assessment once a year to help ensure your systems and site are protected against cyber threats
What is important to know about a network intrusion detection system?
If a network intrusion detection system is installed or to be installed, we recommend that you look for syslog/SIEM messages to understand if there are any cyber attacks being attempted. In addition, vulnerabilities related to Windows OS, tool boxST, QNX OS, CISCO NW switch IOS, and fortigate OS, are updated in our cybersecurity portal. These notifications also include recommendations for software updates, so we recommend you keep an eye out for them, and install software updates/patches as soon as you can once they’re available.
Does isolating your controls systems from one another make your cyber protection stronger?
Controls isolation is becoming less viable as a cybersecurity strategy, in part because there are other mechanisms used by infrastructure managers and adversaries alike to perform the necessary task of moving data into and out of islanded control system networks. These include the use of USB sticks and removable media to bring patches and updates into the control system environment, and to move business data regarding production out to an otherwise unreachable business network. These mechanisms can carry viruses and malware without the knowledge of plant maintenance personnel.
Unfortunately, one of the largest threats comes from inside the power plant, like a disgruntled employee or someone unintentionally connecting a phone or USB port with a virus.
Beyond the risks associated with removable media, there are other potential issues with unexpected connectivity enabled by an adversary, malicious insider, or even an insider acting in good faith but incautiously. Even if wireless networks are forbidden, one of these kinds of actors can easily add wireless access points to the network by plugging it into an unused and unblocked network port. Such wireless access may even be accessible from outside the plant perimeter.
Customer success stories
-
Steam turbine modification
-
Parts derate solution
-
Lowering risk with software
-
Cost-effective generator repair
-
Steam turbine modification
-
Parts derate solution
-
Lowering risk with software
-
Cost-effective generator repair
Steam turbine modification
GE Vernova's Steam Power business recently supported a coal operator in Germany to modify a steam turbine low pressure rotor from a decommissioned site, repurposing it to be installed on their operating unit. Our team adapted the rotor to the new site’s dimensions by removing its coupling and shaft end, and welding on a new stub shaft. This project enabled our customer to save a significant amount of investment in a new rotor to continue operating through the latter stage of their planned life cycle.

Parts derate solution
Our team in the U.S. identified a solution to remove a row of damaged blades from a steam turbine unit, and return it to service safely without them until new parts could be delivered and installed. This type of solution can be applied to a coal site nearing the end of its operating life or having reduced capacity demand, saving significant costs in unneeded replacement parts, while still being able to operate safely.

Lowering risk with software
When a coal operator in the U.K. was looking for a low-cost alternative to extending the life of three generators approaching the end of their life cycles, our team delivered a viable solution. Leveraging software and sensor technology from our portfolio, the operator was able to monitor the units 24/7, and detect potential issues early before a forced shutdown occurs. With this capability, the customer postponed the recommended rewind, and purchased just one rewind kit to limit the costs of continuing to operate the generators in their advanced life cycle stages with lower risk.

Cost-effective generator repair
When deformation and reduced clearance were observed on a generator unit in the Middle East due to coil displacement, the operator needed a cost-effective solution for shorter-term operation. To avoid an inter-turn fault, our team executed a repair allowing the site to continue operating safely with only periodic inspections, but eliminated the cost of a rotor rewind life extension.

Contact us