The HA gas turbine: Advancements in engineering, performance, and efficiency
Som Shantanu
April 02, 2025
8-minute read
Prefer to listen?
This audio content was developed with the use of Generative AI.
In our previous blog, HA gas turbines: Complementing renewables and accelerating the shift toward decarbonization, we addressed the crucial role gas turbines can play in bridging the gap toward decarbonization1, addressing renewable intermittency, and helping to ensure grid stability. High-efficiency gas turbines like the HA gas turbines are crucial in supporting this transition through innovation and technological updates.
The global energy landscape is evolving quickly, driven by electrification and the need to reduce carbon emissions. Gas turbines can help meet these demands with enhanced efficiency, fast and reliable start-up, ramp-up, lower turndown capabilities, and operational flexibility. The adaptability of the high-efficiency HA gas turbine showcases how innovative technologies can address these challenges. As grids worldwide struggle to adapt to the increasing deployment of renewables and the pressures of retiring coal plants, HA gas turbines can provide a reliable and efficient solution.
GE Vernova began developing the H-class technology 26 years ago, the first to introduce it to the industry. The HA gas turbine is developed with decades of engineering expertise, laboratory test validation, and continuous improvement. Its development began by integrating proven features from GE Vernova’s F-class gas turbines and advancements in H-class steam technology.
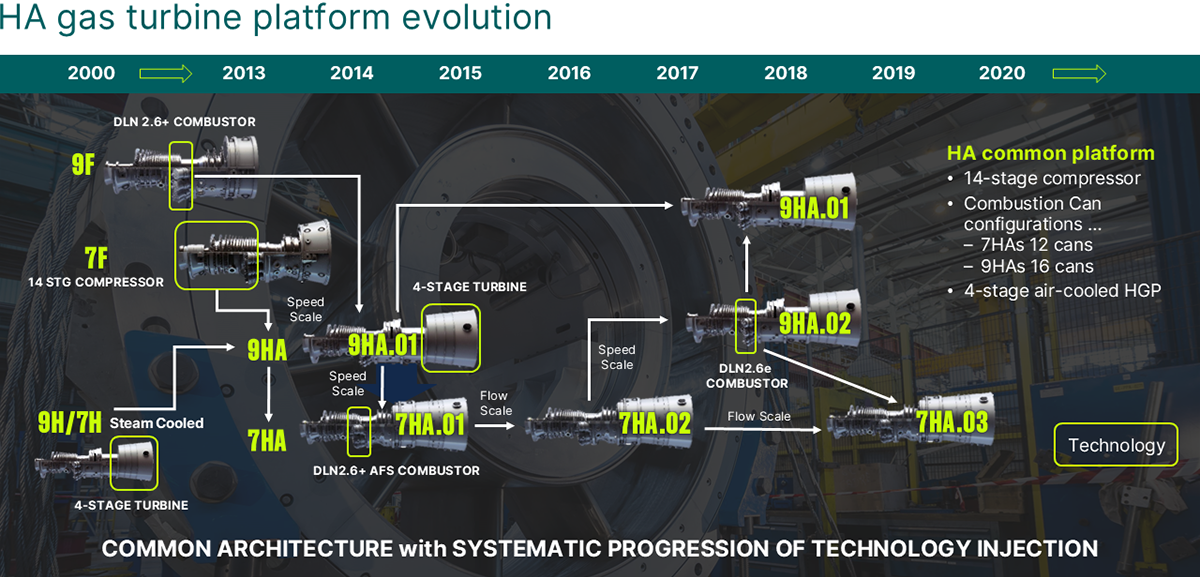
In 2014, the 9HA.01 was launched, combining a 4-stage turbine from steam-cooled 7H and 9H gas turbines and a 14-stage compressor from the 7F.05 gas turbine. Additionally, the 7HA.01 incorporated the DLN 2.6+ combustor with an Axial Fuel Staging (AFS) technology. In 2018, GE Vernova launched the 9HA.02, incorporating the 3D-printed DLN 2.6e combustor system, which can operate on 50% hydrogen blends. GE Vernova’s latest HA technology is the 7HA.03, introduced in 2019 with a 430 MW simple-cycle output. The fleet of high-efficiency HA gas turbines surpassed 3 million operating hours worldwide, showcasing the HA gas turbine's proven reliability. This continuous evolution underscores GE Vernova’s commitment to continuously improving the HA gas turbines to help meet the changing needs of the power industry.
The history of GE Vernova’s HA gas turbine is highlighted by milestones and success stories that showcase innovation, efficiency, and reliability. The timeline below shows how each advancement to the HA gas turbine has brought new capabilities and set global benchmarks:
Today, the HA gas turbine is the world’s fastest-growing fleet in its class, with 176 units ordered by more than 50 customers across 27 countries, helping to meet the diverse demands of today’s energy landscape and customers' needs worldwide.
The HA gas turbine is adaptable and can address various power generation requirements, from peak power and fast ramp-up to achieving minimum emission compliance at lower loads and lower turndown.
To help meet different power generation needs across the industry worldwide, the HA gas turbine offers various solutions, such as combined-cycle and simple-cycle with single or multi-shaft configurations with single or dual fuel capabilities. The 9HA and 7HA simple-cycle gas turbines offer quick start-up and operational flexibility, making the gas turbines ideal for peaking power and emergency backup to a renewable-dominated grid. GE Vernova’s HA gas turbine combined-cycle power plant has industry-leading flexibility and can reach a full combined-cycle plant load in less than 30 minutes while achieving up to 64% efficiency in specific configurations, making it a great complement to intermittent renewable sources.
Additionally, the HA gas turbine's adaptability enables power producers to configure plants according to specific grid and sector needs, helping to ensure flexibility without compromising efficiency. The HA gas turbines are tailored for large-scale, high-efficiency applications, particularly in industries requiring steady baseload power. They are ideal for regions with high renewable penetration, providing rapid ramp-up capabilities to fill gaps left by intermittent power sources.
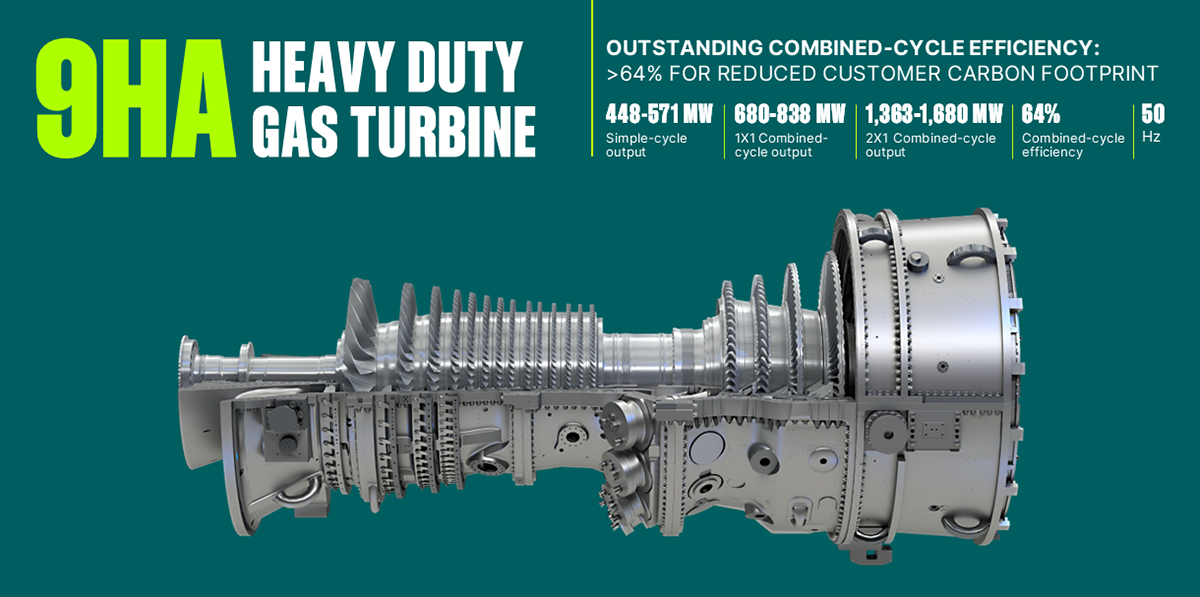
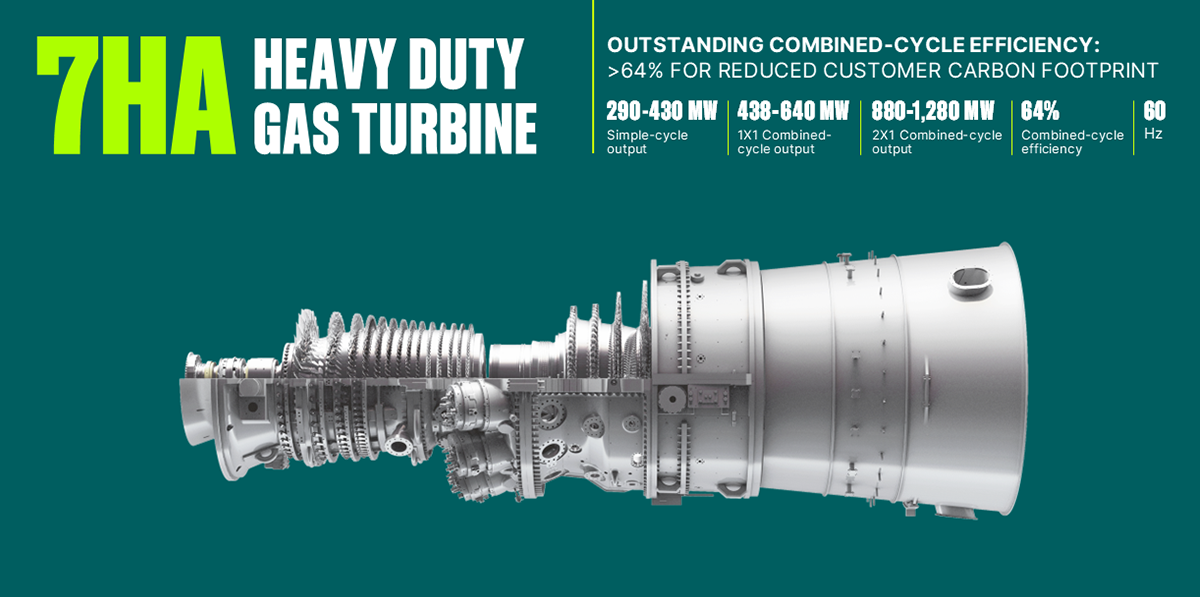
The HA gas turbine showcases how technological evolution can align with sustainability goals. It offers solutions that adapt to diverse grid demands and support renewable integration, helping to ensure that it remains an important part of the energy transition. The growing adoption of HA turbines across Asia, EMEA, and the Americas highlights their global impact. GE Vernova’s ongoing investment in service and repair capabilities, such as the GEVSS facility in Singapore and TGTS in Japan, helps ensure that the HA gas turbine remains operational with reduced downtimes and enhanced lifecycle performance.
Our next blog will explore the HA gas turbine's global reliability and availability, emphasizing its operational performance across diverse geographies and its role in stabilizing power grids worldwide.

Som Shantanu
Executive, Gas Power Engineering Leader -Asia,
GE Vernova Gas Power
As the Asia Engineering Leader, Som is responsible for leading the engineering functions to help deliver on our customer needs and their business priorities, by supporting the entire engineering lifecycle of GE Vernova’s Gas Power technologies in Asia. He, also supports the decarbonization initiative for Asia region, including opportunities in carbon neutral fuels like Hydrogen, Ammonia, and carbon capture technologies, among others.
Discover more
Contact Us